Chemical Engineering Gate Yearwise
Chemical Eng. Gate 2024
Chemical Eng. Gate 2023
Chemical Eng. Gate 2022
Chemical Eng. Gate 2021
Chemical Eng. Gate 2020
Chemical Eng. Gate 2019
Chemical Eng. Gate 2018
Chemical Eng. Gate 2017
Chemical Eng. Gate 2016
Chemical Eng. Gate 2015
Chemical Eng. Gate 2014
Chemical Eng. Gate 2013
Chemical Eng. Gate 2012
Chemical Eng. Gate 2011
Chemical Eng. Gate 2010
Chemical Engineering Gate 2024 Questions with Answer
Ques 1 GATE 2024
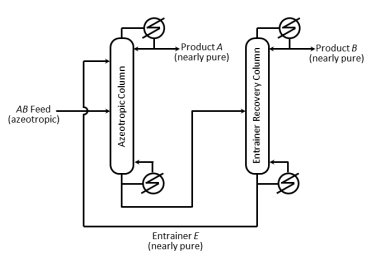
A homogeneous azeotropic distillation process separates an azeotropic AB binary feed using a heavy entrainer, E, as shown in the figure. The loss of E in the two product streams is negligible so that E circulates around the process in a closedcircuit. For a distillation column with fully specified feed(s), given operating pressure, a single distillate stream and a single bottoms stream, the steady-state degrees of freedom equals 2. For the process in the figure with a fully specified AB feed stream and given column operating pressures, the steady-state degrees of freedom equals
Ques 2 GATE 2024
The ratio of the activation energy of a chemical reaction to the universal gas constant is 1000 K. The temperature-dependence of the reaction rate constant follows the collision theory. The ratio of the rate constant at 600 K to that at 400 K is
Ques 3 GATE 2024
The rate of a reaction A → B is 0.2 mol m−3 s−1 at a particular concentration CA1. The rate constant of the reaction at a given temperature is 0.1 m3 mol−1 s−1. If the reactant concentration is increased to 10 CA1 at the same temperature, the reaction rate, in mol m−3 s−1, is
Ques 4 GATE 2024
Two parallel first-order liquid phase reactions A →k1 B and A →k2 C are carried out in a well-mixed isothermal batch reactor. The initial concentration of A in the reactor is 1 kmol m−3, while that of B and C is zero. After 2 hours, the concentration of A reduces to half its initial value, and the concentration of B is twice that of C. The rate constants k1 and k2, in h−1, are, respectively
Ques 5 GATE 2024
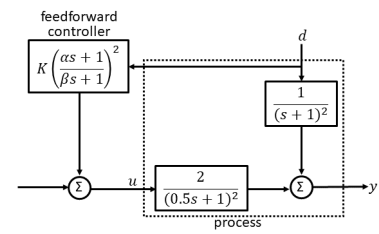
Consider the block diagram in the figure with control input 𝑢, disturbance 𝑑 and output 𝑦. For the feedforward controller, the ordered pair (𝐾, 𝛼⁄𝛽) is
Ques 6 GATE 2024
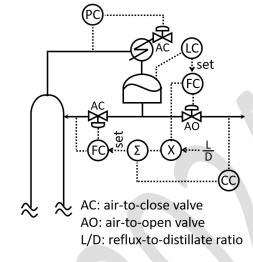
Consider the control structure for the overhead section of a distillation column shown in the figure. The composition controller (CC) controls the heavy key impurity in the distillate by adjusting the setpoint of the reflux flow controller in a cascade arrangement. The sign of the controller gain for the pressure controller (PC) and that for the composition controller (CC) are, respectively,
Ques 7 GATE 2024
In an ammonia manufacturing facility, the necessary hydrogen is generated from methane. The facility consists of the following process units - P: Methanator, Q: CO shift convertor, R: CO2 stripper, S: Reformer, T: Ammonia convertor The correct order of these units, starting from methane feed is
Ques 8 GATE 2024
For the electrolytic cell in a chlor-alkali plant, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Ques 9 GATE 2024
Which of the following statements with reference to the petroleum/petrochemical industry is/are correct?
Ques 10 GATE 2024
Consider the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) in a continuous flow reactor
under steady-state conditions.
The component flow rates at the reactor inlet are:
FN2,0 = 100 mol s−1,
FH2,0 = 300 mol s−1,
Finert,0 = 1 mol s−1.
If the fractional conversion of H2 is 0.60, the outlet flow rate of N2,
in mol s−1, rounded off to the nearest integer, is __________
Ques 11 GATE 2024
Consider a binary mixture of components A and B at temperature T and pressure P.
Let V̄A and V̄B be the partial molar volumes of A and B, respectively.
At a certain mole fraction of A, xA,
(∂V̄A / ∂xA)T,P = 22 cm3 mol−1
and
(∂V̄B / ∂xA)T,P = −18 cm3 mol−1
The value of xA, rounded off to 2 decimal places, is __________
Ques 12 GATE 2024
The capital cost of a distillation column is Rs. 90 lakhs. The cost is to be fully depreciated (salvage value is zero) using the double-declining balance method over 10 years. At the end of two years of continuous operation, the book-value of the column, in lakhs of rupees, rounded off to 1 decimal place, is _______
Ques 13 GATE 2024
Alumina particles with an initial moisture content of 5 kg per kg dry solid are dried in a batch dryer. For the first two hours, the measured drying rate is constant at 2 kg m−2 h−1. Thereafter, in the falling-rate period, the rate decreases linearly with the moisture content. The equilibrium moisture content is 0.05 kg per kg dry solid and the drying area of the particles is 0.5 m2 per kg dry solid. The total drying time, in h, to reduce the moisture content to half its initial value is ______

Total Unique Visitors