Chemical Engineering Gate Yearwise
Chemical Eng. Gate 2024
Chemical Eng. Gate 2023
Chemical Eng. Gate 2022
Chemical Eng. Gate 2021
Chemical Eng. Gate 2020
Chemical Eng. Gate 2019
Chemical Eng. Gate 2018
Chemical Eng. Gate 2017
Chemical Eng. Gate 2016
Chemical Eng. Gate 2015
Chemical Eng. Gate 2014
Chemical Eng. Gate 2013
Chemical Eng. Gate 2012
Chemical Eng. Gate 2011
Chemical Eng. Gate 2010
Chemical Engineering Gate 2025 Questions with Answer
Ques 1 GATE 2025
Consider an enzymatic reaction that follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Let KM. S, and Vmax denote the Michaelis constant, substrate concentration, and maximum reaction rate, respectively. Which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
Ques 2 GATE 2025
Choose the CORRECT ordering of the diameter d of the different types of pores in a solid catalyst.
Ques 3 GATE 2025
Choose the CORRECT statement that describes the dependence of the variance (σΘ2) of the residence time distribution (RTD) with respect to the number of tanks (n) in the Tanks-in-Series model of non-ideal reactors.
Ques 4 GATE 2025
Choose the option that correctly matches the items in Group 1 with those in Group 2.
Group 1
(P) Coking
(Q) Poisoning
(R) Sintering
Group 2
(I) Prolonged exposure of catalyst to high temperature
(II) Deposition of carbonaceous material on catalyst surface
(III) Irreversible chemisorption of molecules on active sites of catalyst
Ques 5 GATE 2025
The residence-time distribution (RTD) function of a reactor (in min-1) is
E(t) = 1-2t, t≤0.5 min; 0, t>0.5 min
The mean residence time of the reactor is ______ min (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
Ques 6 GATE 2025
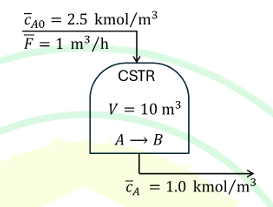
The first-order irreversible liquid phase reaction A→B occurs inside a constant volume (V) isothermal CSTR with the initial steady state conditions shown in the figure. The gain, in kmol/m3 / m3/h, of the transfer function relating the reactor effluent A concentration, cA to the inlet flow rate, F, is
Ques 7 GATE 2025
A zero-order gas phase reaction A→B with rate (-rA)=k=100 mol/(L min) is carried out in a mixed flow reactor of volume 1 L. Pure A is fed to the reactor at a rate of 1 mol/min. At time t=0 the outlet flow is stopped while the inlet flow rate and reactor temperature remain unchanged. Assume that the reactor was operating under steady state before the flow was stopped (t<0). The rate of consumption of A, -dCA/dt, in mol/(L min), at t=1 min is
Ques 8 GATE 2025
The reaction A → products with reaction rate, (-rA)=kCA3, occurs in an isothermal PFR operating at steady state. The conversion (X) at two axial locations (1 and 2) of the PFR is shown in the figure.
The value of l1/l2 is ______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places)
Ques 9 GATE 2025
The catalytic gas phase reaction A → products is carried out in an isothermal batch reactor of 10 L volume using 0.1 kg of a solid catalyst. The reaction is first-order with (-rA)=k''a(t)CA where k''=1 L/(kg catalyst)(h) and CA is the concentration of A in mol/L.
The catalyst activity undergoes first-order decay with rate constant kd=0.01 per hour and a(t).
The reactant conversion after 1 day of operation is ______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
Ques 10 GATE 2025
Methanol is produced by the reversible, gas-phase hydrogenation of carbon monoxide as CO+2H2↔CH3OH.
CO and H2 are charged to a reactor and the reaction proceeds to equilibrium at 453 K and 2 atm. The reaction equilibrium constant, which depends only on the temperature, is 1.68 at the reaction conditions. The mole fraction of H2 in the product is 0.4. Assuming ideal gas behaviour, the mole fraction of methanol in the product is ______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
Ques 11 GATE 2025
Consider the flowsheet in the figure for manufacturing C via the reaction A+B→C in an isothermal CSTR.
The split in the separator is perfect so that the recycle stream is free of C and the product stream is pure C. Let xi denote the mole fraction of species i (i=A,B,C) in the CSTR, which is operated in excess B with xB/xA=4. The reaction is first-order in A with the reaction rate (-rA)=kxxA, where kx=5.0 kmol/(m3h).
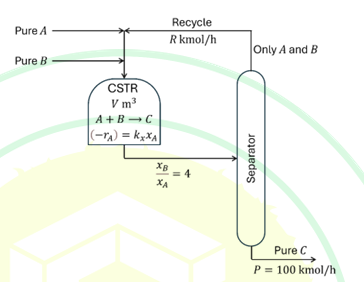
GIVEN: d/dz (z/(1-z)) = 1/(1-z)2.
Ques 12 GATE 2025
To manufacture paper from (i) the (ii) must be freed from the binding matrix of (iii) in the pulping step.
Which one of the following is the CORRECT option to fill in the gaps (i), (ii) and (iii)?', 'Chemical Engineering',
Ques 13 GATE 2025
In the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) from ethylene and chlorine, the sequential order of reactions is

Total Unique Visitors