CS/IT Gate Yearwise
CS/IT Gate 2025 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2024 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2024 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2023
CS/IT Gate 2022
CS/IT Gate 2021 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2021 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2020
CS/IT Gate 2019
CS/IT Gate 2018
CS/IT Gate 2017 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2017 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2016 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2016 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2015 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2015 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2015 (Set 3)
CS/IT Gate 2014 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2014 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2014 (Set 3)
CS and IT Gate 2025 Set-2 Questions with Answer
Ques 1 GATE 2025 SET-2
Consider an unordered list of N distinct integers.
What is the minimum number of element comparisons required to find an integer in the list that is NOT the largest in the list?
We can find an element that is not the largest with just one comparison: take any two elements from the list, compare them, and the smaller one is guaranteed not to be the largest since the other element is larger. Because the integers are distinct, no ties occur. This method works regardless of where the largest element is in the list.
✅ Final Answer: Option (a) — 1.
Reason: The smaller of two compared elements is definitely not the largest, so only one element comparison is needed in the worst case.
Ques 2 GATE 2025 SET-2
Which of the following statements regarding Breadth First Search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) on an undirected simple graph G is/are TRUE?
Ques 3 GATE 2025 SET-2
Let G be an edge-weighted undirected graph with positive edge weights. Suppose a positive constant a is added to the weight of every edge. Which ONE of the following statements is TRUE about the minimum spanning trees (MSTs) and shortest paths (SPs) in G before and after the edge weight update?
Ques 4 GATE 2025 SET-2
A meld operation on two instances of a data structure combines them into one single instance of the same data structure. Consider the following data structures:
P: Unsorted doubly linked list with pointers to the head node and tail node of the list.
Q: Min-heap implemented using an array.
R: Binary Search Tree.
Which ONE of the following options gives the worst-case time complexities for meld operation on instances of size n of these data structures?
Ques 5 GATE 2025 SET-2
An array A of length n with distinct elements is said to be bitonic if there is an index 1≤i≤n such that A[1..i] is sorted in the non-decreasing order and A[i+1..n] is sorted in the non-increasing order.
Which ONE of the following represents the best possible asymptotic bound for the worst-case number of comparisons by an algorithm that searches for an element in a bitonic array A?
Ques 6 GATE 2025 SET-2
Consider the following algorithm someAlgo that takes an undirected graph G as input.

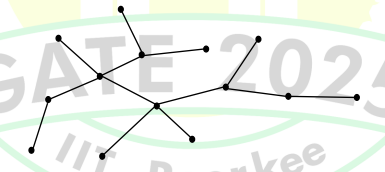
Ques 7 GATE 2025 SET-2
Consider the following statements about the use of backpatching in a compiler for intermediate code generation:
(I) Backpatching can be used to generate code for Boolean expression in one pass.
(II) Backpatching can be used to generate code for flow-of-control statements in one pass.
Which ONE of the following options is CORRECT?
Backpatching is a technique used in compiler intermediate code generation to handle forward jumps when target addresses are not known initially. It allows these addresses to be filled in ("backpatched") later, so code generation can proceed in one pass.
Statement (I): Backpatching allows code generation for Boolean expressions (like those in conditional statements) in one pass, by linking together jump instructions whose targets aren’t known until later.
Statement (II): Backpatching also enables code generation for flow-of-control statements (such as if, while, for) in one pass, by managing jumps for control transfers.
Therefore, both statements are correct.
✅ Final Answer: Option (c) — Both (I) and (II) are correct.
Reason: Backpatching is used for both Boolean expressions and flow-of-control statements so that intermediate code can be generated efficiently in a single pass.
Ques 8 GATE 2025 SET-2
Given the following syntax directed translation rules:
Rule 1: R→AB {B.i = R.i1; A.i=B.i; R.i=A.i+1;}
Rule 2: P→CD {P.i = C.i+D.i; D.i=C.i+2;}
Rule 3: Q→EF {Q.i = E.i+F.i;}
Which ONE is the CORRECT option among the following?
Ques 9 GATE 2025 SET-2
Given a Context-Free Grammar G as follows:
S→Aa|bAc|dc|bda
A→d
Which ONE of the following statements
Ques 10 GATE 2025 SET-2
Consider two grammars G1 and G2 with the production rules given below:
G1: S→if E then S|if E then S else S | a
E→b
G2: S→if E then S|M
M→if E then M else S | c
E→b
where if, then, else, a, b, c are the terminals.
Which of the following option(s) is/are CORRECT?
Ques 11 GATE 2025 SET-2
Consider the following statements:
(i) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) provides a mapping from an IP address to the corresponding hardware (link-layer) address.
(ii) A single TCP segment from a sender S to a receiver R cannot carry both data from S to R and acknowledgement for a segment from R to S.
Which ONE of the following is CORRECT?
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) does provide a mapping from an IP address to the corresponding hardware (link-layer) address, so statement (i) is TRUE.
Statement (ii) is FALSE. A single TCP segment can carry both data from the sender to the receiver and an acknowledgement for a segment that was sent from the receiver to the sender in the same segment. This is called "piggybacking" and is common in bidirectional TCP communication. So, it is not true that a single segment cannot carry both data and acknowledgement.
✅ Final Answer: Option (b) — (i) is TRUE and (ii) is FALSE.
Reason: ARP maps IP addresses to hardware addresses. TCP allows sending data and acknowledgement together, so statement (ii) is incorrect.
Ques 12 GATE 2025 SET-2
Consider the routing protocols given in List I and the names given in List II:
List I
(i) Distance vector routing
(ii) Link state routing
List II
(a) Bellman-Ford
(b) Dijkstra
For matching of items in List I with those in List II, which ONE of the following options is CORRECT?
Correct answer:
a) (i)-(a) and (ii)-(b)
- Distance vector routing (i) uses the Bellman-Ford algorithm (a).
- Link state routing (ii) uses the Dijkstra algorithm (b).
Ques 13 GATE 2025 SET-2
A machine receives an IPv4 datagram. The protocol field of the IPv4 header has the protocol number of a protocol X.
Which ONE of the following is NOT a possible candidate for X?
The protocol field in the IPv4 header is used to indicate the higher-layer protocol to which the payload is delivered. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP), and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) all have assigned protocol numbers in the IPv4 header and can be directly carried in IPv4 datagrams.
However, Routing Information Protocol (RIP) does not have an assigned protocol number in the IPv4 header. RIP is a routing protocol that operates over UDP, so the protocol field would specify UDP (protocol number 17), not RIP itself. Therefore, RIP is NOT a possible candidate for protocol X in an IPv4 header’s protocol field.
✅ Correct Answer: Option (d) — Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
Reason: RIP uses UDP for transport and is not directly specified in the IPv4 protocol field, while ICMP, IGMP, and OSPF can be.

Total Unique Visitors