CS/IT Gate Yearwise
CS/IT Gate 2025 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2024 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2024 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2023
CS/IT Gate 2022
CS/IT Gate 2021 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2021 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2020
CS/IT Gate 2019
CS/IT Gate 2018
CS/IT Gate 2017 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2017 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2016 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2016 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2015 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2015 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2015 (Set 3)
CS/IT Gate 2014 (Set 1)
CS/IT Gate 2014 (Set 2)
CS/IT Gate 2014 (Set 3)
CS and IT Gate 2014 Set-1 Questions with Answer
Ques 27 GATE 2014 SET-1
Consider the following pseudocode. What is the total number of multiplications to be performed?
D = 2
for i = 1 to n do
for j = i to n do
for k = j + 1 to n do
D = D * 3
Ques 28 GATE 2014 SET-1
Consider the relation scheme
R = (E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N)
and the set of functional dependencies {{E, F} → {G}, {F} → {I, J}, {E, H} → {K, L}, {K} → {M}, {L} → {N}}. Which of the following is a key for R?
Ques 29 GATE 2014 SET-1
Given the following statements:
S1: A foreign key declaration can always be replaced by an equivalent check assertion in SQL.
S2: Given the table R(a, b, c) where a and b together form the primary key, the following is a valid table definition.
CREATE TABLE S(
d INT,
e INT,
PRIMARY KEY (d),
FOREIGN KEY (a) REFERENCES R
)
Which one of the following statements is CORRECT?
Ques 30 GATE 2014 SET-1
Consider the following four schedules due to three transactions (indicated by the subscript) using read and write on a data item x, denoted by r(x) and w(x) respectively. Which one of them is conflict serializable?
(A) r1(x); r2(x); w1(x); r3(x); w2(x)
(B) r2(x); r1(x); w2(x); r3(x); w1(x)
(C) r3(x); r2(x); r1(x); w2(x); w1(x)
(D) r2(x); w2(x); r3(x); r1(x); w1(x)
Ques 31 GATE 2014 SET-1
Given the following two statements:
S1: Every table with two single-valued attributes is in 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF.
S2: AB → C, D → E, E → C is a minimal cover for the set of functional dependencies AB → C, D → E, AB → E, E → C.
Which one of the following is CORRECT?
Ques 32 GATE 2014 SET-1
Given the following schema:
employees(emp-id, first-name, last-name, hire-date, dept-id, salary)
departments(dept-id, dept-name, manager-id, location-id)
You want to display the last names and hire dates of all latest hires in their respective departments in the location ID 1700. You issue the following query:
SQL> SELECT last-name, hire-date
FROM employees
WHERE (dept-id, hire-date) IN (SELECT dept-id, MAX(hire-date) FROM employees JOIN departments USING(dept-id) WHERE location-id = 1700 GROUP BY dept-id);
What is the outcome?
Ques 33 Gate 2014 Set-1
Let P be a QuickSort Program to sort numbers in ascending order using the first element as pivot. Let t1 and t2 be the number of comparisons made by P for the inputs [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and [4, 1, 5, 3, 2] respectively. Which one of the following holds?
Ques 34 GATE 2014 SET-1
Consider the 4-to-1 multiplexer with two select lines S1 and S0 given below.
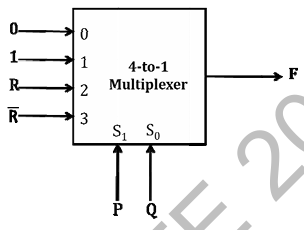
Ques 35 GATE 2014 SET-1
Which one of the following propositional logic formulas is TRUE when exactly two of p, q, and r are TRUE?
Ques 36 Gate 2014 Set-1
Consider the following Boolean expression for F:
F(P, Q, R, S) = PQ + P'QR + P'QR'S
The minimal sum-of-products form of F is__________
Ques 37 Gate 2014 Set-1
Consider the statement
“Not all that glitters is gold”
Predicate glitters(x) is true if x glitters and predicate gold(x) is true if x is gold. Which one of the following logical formulae represents the above statement?
Ques 38 GATE 2014 SET-1
A pennant is a sequence of numbers, each number being 1 or 2. An n-pennant is a sequence of numbers with sum equal to n. For example, (1, 1, 2) is a 4-pennant. The set of all possible 1-pennants is {(1)}, the set of all possible 2-pennants is {(2), (1, 1)} and the set of all 3-pennants is {(2, 1), (1, 1, 1), (1, 2)}. Note that the pennant (1, 2) is not the same as the pennant (2, 1). The number of 10-pennants is _______.
Ques 39 GATE 2014 SET-1
Let S denote the set of all functions f: {0, 1}4 → {0, 1}. Denote by N the number of functions from S to the set {0, 1}. The value of log2log2N is _______.

Total Unique Visitors