Chemical Engineering Gate Yearwise
Chemical Eng. Gate 2024
Chemical Eng. Gate 2023
Chemical Eng. Gate 2022
Chemical Eng. Gate 2021
Chemical Eng. Gate 2020
Chemical Eng. Gate 2019
Chemical Eng. Gate 2018
Chemical Eng. Gate 2017
Chemical Eng. Gate 2016
Chemical Eng. Gate 2015
Chemical Eng. Gate 2014
Chemical Eng. Gate 2013
Chemical Eng. Gate 2012
Chemical Eng. Gate 2011
Chemical Eng. Gate 2010
Chemical Engineering Gate 2011 Questions with Answer
Ques 40 GATE 2011
A transporter receives the same number of orders each day. Currently, he has some pending orders (backlog) to be shipped. If he uses 7 trucks, then at the end of the 4th day he can clear all the orders. Alternatively, if he uses only 3 trucks, then all the orders are cleared at the end of the 10th day. What is the minimum number of trucks required so that there will be no pending order at the end of the 5th day?
Ques 41 GATE 2011
Consider two black bodies with surfaces S1 (area=1m2) and S2 (area=4 m2). They exchange heat only by radiation. 40% of the energy emitted by SI is received by S2. The fraction of energy emitted by S2 that is received by S1 is
Ques 42 GATE 2011
In film type condensation over a vertical tube, local heat transfer coefficient is
Ques 43 GATE 2011
Oil at 120°C is used to heat water at 30°C in a 1-1 co-current shell and tube heat exchanger. The available heat exchange area is S1. The exit temperatures of the oil and the water streams are 90°C and 60°C respectively. The co-current heat exchanger is replaced by a 1-1 counter-current heat exchanger having heat exchange area S2. If the exit temperatures and the overall heat transfer coefficients are same, the ratio of S1 to S2 is
Ques 44 GATE 2011
Heat is generated uniformly within a solid slab. The slab separates fluid 1 from fluid 2. The heat transfer coefficients between the solid slab and the fluids are h1 and h2(h2>h1) respectively. The steady state temperature profile (T vs. x) for one-dimensional heat transfer is CORRECTLY shown by
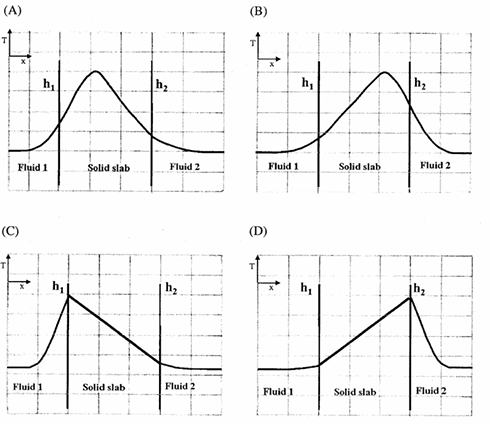
Ques 45 GATE 2011
A PID controller output p(t), in time domain, is given by p(t)=30+5e(t)+1.25∫0te(t)dt+15(de(t)/dt) where e(t) is the error at time t. The transfer function of the process to be controlled is Gp(s)=10/(200s+1). The measurement of the controlled variable is instantaneous and accurate.
The transfer function of the controller is
Ques 46 GATE 2011
A PID controller output p(t), in time domain, is given by p(t)=30+5e(t)+1.25∫0te(t)dt+15(de(t)/dt) where e(t) is the error at time t. The transfer function of the process to be controlled is Gp(s)=10/(200s+1). The measurement of the controlled variable is instantaneous and accurate.
The characteristic equation of the closed loop is
Ques 47 GATE 2011
Match the process parameters in Group I with the measuring instruments in Group II
GROUP I
P. Flame temperature
Q. Composition of LPG
R. Liquid air temperature
GROUP II
I. Thermocouple
II. Radiation pyrometer
III. Gas chromatograph
Ques 48 GATE 2011
The range of standard current signal in process instruments is 4 to 20 mA. Which ONE of the following is the reason for choosing the minimum signal as 4 mA instead of 0 mA?
Ques 49 GATE 2011
The following diagram shows a CSTR with two control loops. A liquid phase, endothermic reaction is taking place in the CSTR, and the system is initially at steady state. Assume that the changes in physical properties of the system are negligible.
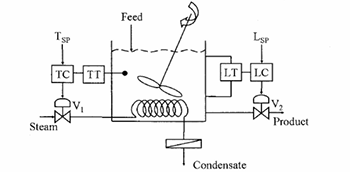
Which ONE of the following statements is TRUE?
Ques 50 GATE 2011
Ammonia is synthesised at 200 bar and 773 K by the reaction N2+3H2↔2NH3. The yield of ammonia is 0.45 mol/mol of fresh feed. Flow sheet for the process (along with available compositions) is shown below.
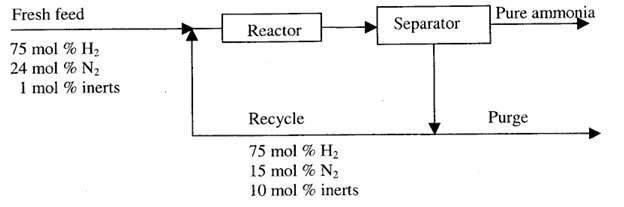
Ques 51 GATE 2011
The following combustion reactions occur when methane is burnt.
CH4+2O2→CO2+2H2O
2CH4+3O2→2CO+4H2O
20% excess air is supplied to the combustor. The conversion of methane is 80% and the molar ratio of CO to CO2 in the flue gas is 1:3. Assume air to have 80 mol % N2 and rest O2. The O2 consumed as a PERCENTAGE of O2 entering the combustor is
Ques 52 GATE 2011
Simultaneous heat and mass transfer is occurring in a fluid flowing over a flat plate. The flow is laminar. The concentration boundary layer will COINCIDE with the thermal boundary layer, when

Total Unique Visitors