Mechanical Engineering Gate Yearwise
Mechanical Engineering Gate 2013 Set-2 Questions with Answer
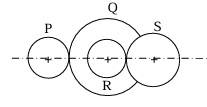
Ques 53 GATE 2013 SET-2
A compound gear train with gears P, Q, R and S has number of teeth 20, 40, 15 and 20, respectively. Gears Q and R are mounted on the same shaft as shown in the figure. The diameter of the gear Q is twice that of the gear R. If the module of the gear R is 2 mm, the center distance in mm between gears P and S is
Ques 54 GATE 2013 SET-2
A flywheel connected to a punching machine has to supply energy of 400 Nm while running at a mean angular speed of 20 rad/s. If the total fluctuation of speed is not to exceed ±2%, the mass moment of inertia of the flywheel in kg-m2 is
Ques 55 GATE 2013 SET-2
A steel ball of diameter 60 mm is initially in thermal equilibrium at 1030°C in a furnace. It is suddenly removed from the furnace and cooled in ambient air at 30°C, with convective heat transfer coefficient h = 20 W/m2K. The thermo-physical properties of steel are: density ρ=7800 kg/m3, conductivity k=40 W/mK and specific heat c=600 J/kgK. The time required in seconds to cool the steel ball in air from 1030°C to 430°C is
Ques 56 GATE 2013 SET-2
Water is coming out from a tap and falls vertically downwards. At the tap opening, the stream diameter is 20 mm with uniform velocity of 2 m/s. Acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s2. Assuming steady, inviscid flow, constant atmospheric pressure everywhere and neglecting curvature and surface tension effects, the diameter in mm of the stream 0.5 m below the tap is approximately
Ques 57 GATE 2013 SET-2
Specific enthalpy and velocity of steam at inlet and exit of a steam turbine, running under steady state, are as given below:
| Specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) | Velocity (m/s) | |
| Inlet steam condition | 3250 | 180 |
| Exit steam condition | 2360 | 5 |
The rate of heat loss from the turbine per kg of steam flow rate is 5 kW. Neglecting changes in potential energy of steam, the power developed in kW by the steam turbine per kg of steam flow rate, is
Ques 58 GATE 2013 SET-2
Water (specific heat, cp = 4.18 kJ/kgK) enters a pipe at a rate of 0.01 kg/s and a temperature of 20°C. The pipe, of diameter 50 mm and length 3 m, is subjected to a wall heat flux q"w in W/m2.
If q"w = 2500x, where x is in m and in the direction of flow (x=0 at the inlet), the bulk mean temperature of the water leaving the pipe in °C is
Ques 59 GATE 2013 SET-2
Water (specific heat, cp = 4.18 kJ/kgK) enters a pipe at a rate of 0.01 kg/s and a temperature of 20°C. The pipe, of diameter 50 mm and length 3 m, is subjected to a wall heat flux q"w in W/m2.
If q"w = 5000 and the convection heat transfer coefficient at the pipe outlet is 1000 W/m2K, the temperature in °C at the inner surface of the pipe at the outlet is
Ques 60 GATE 2013 SET-2
A single riveted lap joint of two similar plates has the following geometrical and material details:
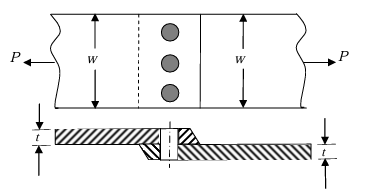
If the rivets are to be designed to avoid crushing failure, the maximum permissible load P in kN is
Ques 61 GATE 2013 SET-2
A single riveted lap joint of two similar plates has the following geometrical and material details:

If the plates are to be designed to avoid tearing failure, the maximum permissible load P in kN is
Ques 62 GATE 2013 SET-2
In a simple Brayton cycle, the pressure ratio is 8 and temperatures at the entrance of compressor and turbine are 300 K and 1400 K, respectively. Both compressor and gas turbine have isentropic efficiencies equal to 0.8. For the gas, assume a constant value of cp (specific heat at constant pressure) equal to 1 kJ/kgK and ratio of specific heats as 1.4. Neglect changes in kinetic and potential energies.
The power required by the compressor in kW/kg of gas flow rate is
Ques 63 GATE 2013 SET-2
In a simple Brayton cycle, the pressure ratio is 8 and temperatures at the entrance of compressor and turbine are 300 K and 1400 K, respectively. Both compressor and gas turbine have isentropic efficiencies equal to 0.8. For the gas, assume a constant value of cp (specific heat at constant pressure) equal to 1 kJ/kgK and ratio of specific heats as 1.4. Neglect changes in kinetic and potential energies.
The thermal efficiency of the cycle in percentage (%) is
Ques 64 GATE 2013 SET-2
In orthogonal turning of a bar of 100 mm diameter with a feed of 0.25 mm/rev, depth of cut of 4 mm and cutting velocity of 90 m/min, it is observed that the main (tangential) cutting force is perpendicular to the friction force acting at the chip-tool interface. The main (tangential) cutting force is 1500 N.
The orthogonal rake angle of the cutting tool in degree is
Ques 65 GATE 2013 SET-2
In orthogonal turning of a bar of 100 mm diameter with a feed of 0.25 mm/rev, depth of cut of 4 mm and cutting velocity of 90 m/min, it is observed that the main (tangential) cutting force is perpendicular to the friction force acting at the chip-tool interface. The main (tangential) cutting force is 1500 N.
The normal force acting at the chip-tool interface in N is

Total Unique Visitors